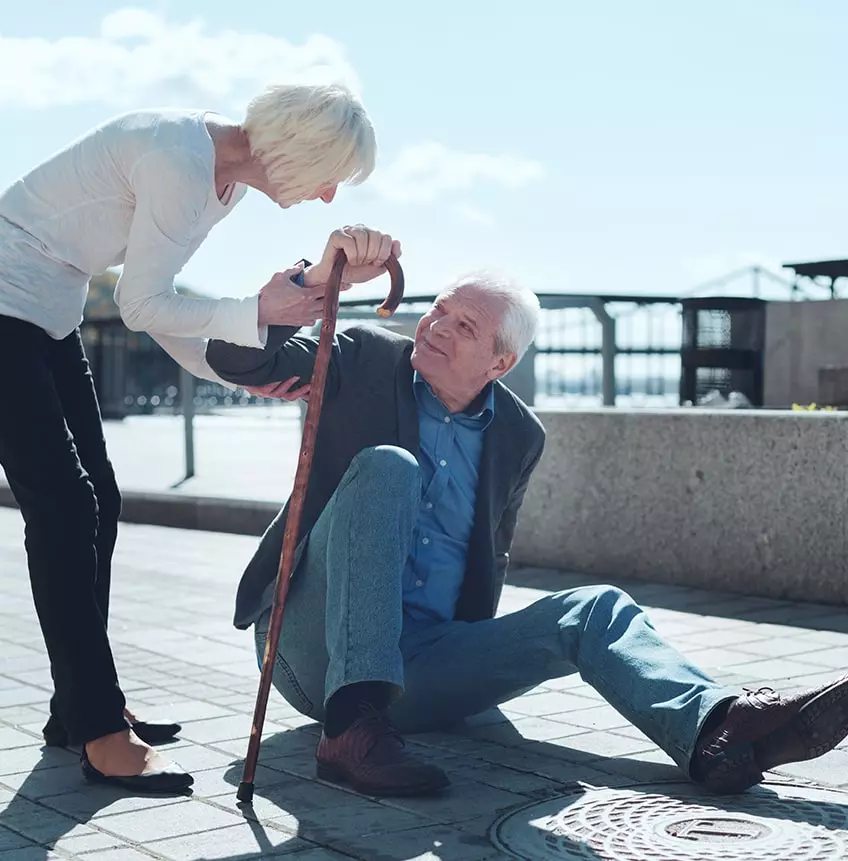
Vulnerability can arise gradually or suddenly. Age, illness, disability, or cognitive decline may limit a person’s ability to protect themselves from harm, neglect, or exploitation. In the UK, a robust legal framework exists to ensure that vulnerable adults are protected, supported, and treated with dignity.
Understanding what legal protections exist for vulnerable adults helps families recognise when intervention is required and how the law supports action rather than silence.
Who Is Considered a Vulnerable Adult?
Find YOUR ideal care home NOW!
A vulnerable adult is someone who may be unable to protect themselves from harm or abuse due to physical, mental, or emotional limitations. Vulnerability is situational rather than permanent and may fluctuate over time.
Legal protection focuses on risk and capacity, not labels.
Why Legal Protections Matter
Legal safeguards exist to prevent abuse, neglect, and avoidable harm. They also ensure that decisions affecting vulnerable adults respect autonomy wherever possible while intervening decisively when safety is at risk.
These protections balance freedom with protection, ensuring that support is proportionate and justified.
Core Legal Protections for Vulnerable Adults in the UK
UK law provides multiple layers of protection that work together rather than in isolation.
Key Legal Safeguards Explained
| Legal Protection | What It Covers | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Safeguarding duties | Protection from abuse and neglect | Ensures action when harm is suspected |
| Mental capacity protections | Decision-making rights and assessments | Prevents unlawful or coercive decisions |
| Best interests framework | Decisions made when capacity is lacking | Centres wellbeing and dignity |
| Right to advocacy | Independent representation | Gives vulnerable adults a voice |
| Duty of care | Legal obligation to prevent foreseeable harm | Holds services accountable |
Safeguarding Law and Protection From Harm
Safeguarding laws require action when a vulnerable adult is at risk of abuse, neglect, or exploitation. Abuse may be physical, emotional, financial, or psychological, and neglect may involve failure to meet basic needs.
Safeguarding focuses on prevention as much as response. Early reporting is encouraged to stop harm before it escalates.
Mental Capacity and Decision-Making Rights
Mental capacity law protects the right to make decisions wherever possible. Capacity is decision-specific and time-specific, meaning a person may be able to make some decisions but not others.
When capacity is lacking, decisions must be made in the individual’s best interests, with consultation and careful consideration of risks and preferences.
Protection Against Unlawful Restrictions
Vulnerable adults are protected from unnecessary or disproportionate restrictions on their freedom. Any limitation must be justified, proportionate, and regularly reviewed.
This ensures that safety measures do not become excessive or punitive.
The Role of Advocacy
Independent advocacy supports vulnerable adults who may struggle to express concerns or understand decisions. Advocates help ensure that rights are respected and that voices are heard during assessments, reviews, and safeguarding processes.
Advocacy is a legal safeguard, not a courtesy.
How Families Are Protected and Involved
Families have the right to raise concerns, request reviews, and participate in safeguarding discussions. Legal frameworks recognise families as key partners in protecting vulnerable adults.
Challenging decisions is not interference; it is a recognised right.
When Legal Protections Should Be Activated
Legal protections should be activated whenever there is reasonable concern about harm, neglect, or decision-making that does not reflect a person’s best interests.
Waiting for proof of harm can increase risk. The law supports action based on credible concern.
Why Knowing the Law Empowers Families
Families who understand legal protections are better equipped to advocate effectively. Knowledge reduces fear of speaking up and ensures that concerns are framed in terms of rights and safety rather than complaint.
The law exists to support protection, not silence.
FAQ – Legal Protections for Vulnerable Adults
What legal protections exist for vulnerable adults in the UK?
Safeguarding laws, mental capacity protections, advocacy rights, and duty of care obligations.
Who decides if someone is vulnerable?
Vulnerability is based on risk and ability to protect oneself, not age alone.
Can families trigger safeguarding protections?
Yes. Families can raise safeguarding concerns.
Are vulnerable adults protected from emotional harm?
Yes. Emotional and psychological harm are covered by safeguarding law.
Do legal protections remove personal autonomy?
No. They aim to preserve autonomy while reducing risk.
Need help finding a care home?
Senior Home Plus offers free personalized guidance to help you find a care facility that suits your health needs, budget, and preferred location in the UK.
Call us at 0203 608 0055 to get expert assistance today.
Search for Care Homes by Region in the UK
| East Midlands | Eastern | Isle of Man |
| London | North East | North West |
| Northern Ireland | Scotland | South East |
| South West | Wales | West Midlands |
| Yorkshire and the Humber |
You are looking for a care home or nursing home for your loved one ?
Share this article :
Latest posts
You are looking for an establishment for your loved one ?
Get availability & prices
Fill in this form and receive
all the essential information
We would like to inform you of the existence of the opposition list for telephone canvassing.